In an era where businesses generate terabytes of data daily and upgrade hardware every few years, the end-of-life management of IT assets has never been more critical. Consider this: the global IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) market was valued at $17.4 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a 7.7% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) through the decade, driven by escalating concerns over data security and electronic waste (e-waste). Yet, many organizations still treat outdated servers, laptops, and storage devices as mere trash, risking data breaches, regulatory fines, and environmental harm.
It is time to begin the IT Asset Disposition (ITAD)–a complete, safe and secure process that goes beyond the simple disposal. ITAD makes sure that the discarded IT equipment is properly handled and maximizes value while reducing risk. It’s for businesses. ITAD isn’t an option, but a strategic necessity that protects data and complies with the law that promote sustainability, and improves profitability.
In this article we’ll go over the basics of what ITAD is, the step-by-step process, why it’s crucial to your business and the best way to successfully implement it.
What is IT Asset Disposition (ITAD)?
IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) is the method of retirement, recycling, repurposing, or disposing of old and surplus IT resources in a responsible manner. These include equipment like servers, computer network equipment, portable devices, software licenses, and the sensitive information they hold. In contrast to haphazard disposal, such as throwing devices in the waste or selling them to the secondary market without security measures–ITAD puts a high priority on three principles including security of data, regulatory compliance and recovery of resources.
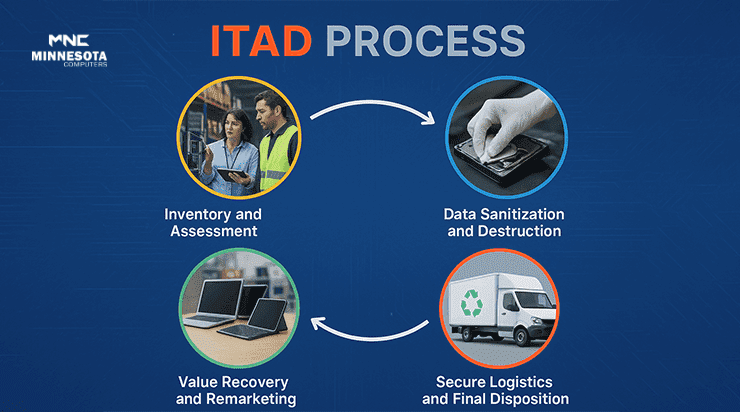
The ITAD Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing ITAD isn’t a single-time event It’s a systematic procedure designed to be traceable and accountability. This is how it usually unfolds making sure that no asset gets lost between the cracks.
Step 1: Inventory and Assessment
Begin by conducting an review of all your IT assets. Utilizing ITAM software catalog devices, assess their condition, and evaluate their residual value. Does the laptop have a market value? Does the server include confidential information? This step identifies potential risks such as non-compliant storage media and provides the basis for decisions in the future.
Step 2: Data Sanitization and Destruction
Security is the most important factor. Data deletion follows the same standards as the Special Publication 800-88 of NIST, which outlines techniques such as overwriting and desgaussing (for magnetic media) and physical shredding of drives that are in their last stages. Certified companies provide destruction certifications, which prove conformity and providing audit reports. In the absence of this, businesses could be exposed to data breaches. Remember that the price of data security incident was $4.45 million in 2023.
Step 3: Value Recovery and Remarketing
Many assets aren’t intended for scrap. Equipment that is functional can be repaired and then sold, donated, or leased to be used again. Recycling helps recover precious metals like copper, gold or rare earth elements, transforming the waste into profit. Many providers handle this through programs that may recover 10% to 30% of the asset’s value, based on its condition.
Step 4: Secure Logistics and Final Disposition
Transporting valuables using GPS-tracked secured vehicles to stop the theft of or tampering with. For items that are not recyclable Ethical disposal is in compliance with the laws governing electronic waste that divert the majority of materials from landfills using certified recyclers. A complete chain-of custody document closes the loop and is available for review by regulatory authorities.
Why ITAD is Essential for Businesses: Key Benefits
In the digital age, it is imperative to take care of ITAD; it’s not just unprofessional, it’s vulnerable. The reason why innovative companies take ITAD seriously with tangible benefits.
1. Enhanced Data Security
The retired devices often contain sensitive data: documents of customers, intellectual property or financial information. Incorrect disposal can lead to data incidents of data breaches, which result in 60% of breaches linked to stolen or lost hardware. For instance, healthcare organizations employing ITAD can avoid HIPAA breaches, which can result in penalties that can reach $1.5 million for each violation.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Global regulations are becoming stricter. GDPR in Europe requires the deletion of data that cannot be recovered and penalties that can reach four percent of annual revenue. The U.S., HIPAA, CCPA and FACTA require similar protections, and EPA regulations regulate e-waste. ITAD guarantees compliance, minimizing the risk of legal liability and simplifying audits. Non-compliance? Expect fines averaging $14.8 million for major breaches.
3. Environmental Sustainability
ITAD promotes a circular economic model by recycling 95 percent of the components, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and reducing the use of resources. This is in line with the company’s ESG goals, attracting green-minded stakeholders and earning eco-friendly incentives.
4. Financial Gains and Cost Efficiency
ITAD isn’t cheap when first purchased, but it is a good investment. Businesses can recover the value of their investments through resales (up to 50% return on old assets) and can avoid the storage/maintenance cost for equipment that is no longer in use. The market’s projected growth to $24.5 billion before 2026 demonstrates the potential for ROI. In addition, it lowers TCO because it allows for timely technology refreshes and boosts productivity.
5. Risk Mitigation and Operational Streamlining
Beyond the four big players, ITAD fosters resilience. It reduces disruptions to supply chains through reclaiming materials and improves the image of companies by enhancing their status through CSR reporting. Integrated with ITAM, It provides the ability to monitor in real time and prevents the spread of assets.
The Future of ITAD: Trends Shaping Tomorrow’s Practices
In 2025 year, Blockchain and AI will increase the traceability of an asset, that predict its life-cycle end with 90 percent accuracy. The stricter regulations, such as increased EU directives on e-waste require global compliance and circular economies push zero-waste strategies.
For companies that are in the business of integrating ITAD with sustainability tools, making preparations for multinational operations and utilizing it as an advantage. When e-waste reaches 82 million tonnes by 2030 and is proactive, ITAD will distinguish the leaders from the laggards.
Conclusion
IT Asset Disposition isn’t a box to check but rather safeguarding your company’s integrity. By creating clear processes for safe erase, value recovery, and sustainable removal, ITAD shields against breaches, fines, and waste while also gaining financial and reputational value. In a world of continuous technology churn, failing to recognize it can lead to disaster, whereas accepting it can build the ability to endure.
FAQs
- What is the difference between ITAD and ITAM? ITAM manages the full lifecycle of assets, while ITAD focuses on the disposition phase, ensuring secure end-of-life handling.
- How much value can businesses recover through ITAD? Typically 10-50%, via resale or recycling, depending on asset condition and market demand.
- What certifications should I look for in an ITAD provider? Key ones include R2v3 for responsible recycling, NAID AAA for data destruction, and e-Stewards for ethical e-waste management.
- Is ITAD only for large enterprises? No—small and mid-sized businesses benefit equally, with scalable services matching their needs.
- How does ITAD support sustainability goals? It diverts 90%+ of e-waste from landfills through recycling, aligning with ESG standards and reducing carbon footprints.
- What are the risks of skipping ITAD? Data breaches, fines (e.g., up to 4% of revenue under GDPR), and environmental penalties.
- How long does the ITAD process take? 1-4 weeks, depending on volume, but planning ahead minimizes disruptions.






Most businesses utilize a network connection to some degree, be it internal data storage or an online point of sale system. While larger corporations often have complex data security systems in place, small businesses can also fall victim to a cyber attack if they do not take steps to protect themselves.